- publish
A verification email has been sent.
Thank you for registering.
An email containing a verification link has been sent to .
Please check your inbox.
An account with your email already exists.
Strategies to manage the implementation of uncleared margin rules in Australia
- Tue 06 July 2021
The rollout of the uncleared margin rules – which has been co-ordinated by regulators globally (including APRA in Australia) - has led to firms putting in place programmes of work to manage the implementation. These programmes cover everything from regulatory model approval, a focussed approach to managing average aggregate notional amount (AANA) levels, counterparty exposure and threshold management to optimising access to liquidity.
With compliance dates for phase 5 and 6 firms fast approaching, we provide insight into the implementation of the rules in Australia and review some of the strategies that firms are putting in place.
A recap: who is captured and when?
Regulators require users of non-cleared OTC derivatives to bilaterally agree and exchange initial margins (IM) with their counterparties that is triggered through an IM threshold of A$75m on a per counterparty basis. This is being implemented via a phased-in approach where a firm’s AANA exceeds associated qualifying levels.
The model below depicts the phased in qualifying levels and timing from an Australian regime (APRA) perspective.
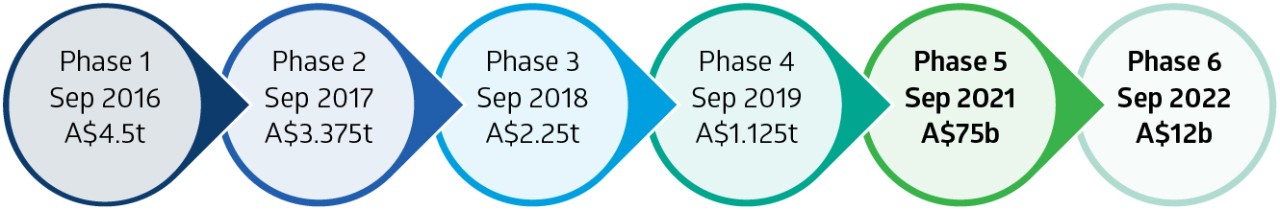
Substantial progress has been made to date with the largest users of non-cleared derivatives now captured under the APRA Prudential Standard CPS 226 Prudential Standard and Phases 1 - 4.
Firms that may be captured under either phase 5 or phase 6 qualifying levels are seeking to address a couple of key questions relating to their business:
- Will my AANA exceed the phase 5 or phase 6 qualifying levels? (Calculations are based across March, April and May aggregate notional each year); and
- Will my IM exposure with counterparties exceed the counterparty IM threshold? (Only new trades from 1 September in year of commencing are counted towards the IM threshold).
Greater complexity exists for phase 5 and 6 readiness
A challenge for phase 5 and phase 6 firms - that are generally considered buy-side - is the sheer proliferation of firms impacted versus previous phases. This magnifies the impact to all related parties; from trading counterparties to custodians and asset managers trading for asset owners. To ensure timeframes are adhered to, focus must also be placed on activities such as regulatory approval of risk models and collateral management, amongst other required support services.
The industry guidance of 12 to 18 months for readiness is a key indicator of the many complexities associated with being in an operationally capable state to exchange IM under the uncleared margin rules.
The phased-in approach has generally meant that support across all related parties is also occurring phase by phase e.g. the ability for phase 6 firms to get full traction while phase 5 is yet to be implemented is sometimes limited and phase 6 firms should factor this into their planning.
Strategies for efficient derivative portfolio management
Where firms are running against the regulatory clock, they are looking at how to manage the many unknowns. Time constraints from counterparties, custodians and other key providers are driving considered and active management of OTC derivatives trading to manage the impact of uncleared margin rules.
Whether taking a short- or longer-term view and without taking an extreme approach to significantly reducing their OTC derivatives trading activity, firms may consider a number of strategies.
- Reducing their AANA.
- Compress existing non-cleared OTC derivatives exposures across counterparties to reduce aggregate/gross notional value.
- Backloading of non-cleared OTC derivatives with counterparties to become cleared OTC derivatives (falling outside AANA calculation).
2. Remaining under counterparty IM exchange threshold levels.
- Set and monitor IM limits with counterparties to remain under the IM threshold that triggers the exchange of IM.
- Trade OTC derivatives with counterparties on a cleared basis.
- Utilise exchange traded futures in replacement of OTC derivatives where suitable.
Optimise your trading book and access to liquidity
Firms are increasingly optimising their trading book and access to liquidity by:
- Accessing pre-trade margin calculation tools when evaluating their derivatives strategy. Differences exist between bilateral and cleared margin resulting in different costs to fund those margins and opportunities to reduce funding drag.
- Accessing a broader range of counterparties. This can be achieved via centrally clearing or trading listed derivatives as the counterparty credit risk is removed and access to liquidity is greatly enhanced.
- Reviewing the efficiencies and benefits of clearing versus remaining bilateral, with special consideration of assessing which CCP(s) they will access, based on their requirements.
Joris Hillmann, Head of Capital Markets for AustralianSuper, comments:
“The uncleared margin rules brought about added complexity and cost for both monitoring and maintaining initial margin exposures for non-cleared OTC derivatives across multiple counterparties. Due to long on-boarding lead times, counterparties may be more selective on who they will put these full arrangements in place with. During times of market stress the ability to move quickly and document with counterparties in line with uncleared margin rules is limited and that impacts our access to liquidity. Being able to trade on a cleared basis improves our access to overall market liquidity both in normal and stressed market conditions.”
Phase 5 and 6 firms have options to manoeuvre within or around the rules. Firms will continue to make decisions on how to best approach the impact of uncleared margin rules depending on their own business drivers. Central clearing of OTC derivatives has been used by the dealer-to-dealer community for many years, facilitating ongoing service innovation, a progressive broadening of the range of clearable OTC products and growing liquidity accessible via OTC clearing services.
OTC and futures clearing provide a key risk management tool when managing derivatives trading. This was outlined by global regulators with one of their original drivers for uncleared margin rules to support further use of centrally cleared derivatives. It is crucial that firms look to access clearing as a part of their own overall risk management approach.
About the author
Market insights , ASX
Disclaimer:
Independent advice from an Australian financial services licensee is needed before making financial decisions. This is not intended to be financial product advice. To the extent permitted by law, ASX Limited ABN 98 008 624 691 and its related bodies corporate excludes all liability for any loss or damage arising in any way including by way of negligence.
© Copyright ASX Operations Pty Limited ABN 42 004 523 782. All rights reserved 2021.