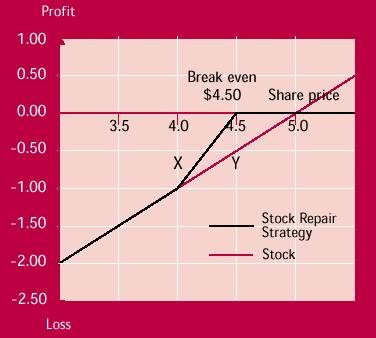
Profits and losses
The stock repair strategy is designed to allow investors to break-even more quickly on a losing stock position. It does not involve investing more cash or increasing the risk of the position.
The strategy combines a losing stock position with a ratio call spread where twice as many calls are sold as are bought. Unlike the ratio call spread the investor is not exposed to unlimited losses on any of the written calls. The written call options are covered either by the long stock position or by the bought call. Ideally, the spread is opened at no cost, or for a credit, with the premium received from the calls written at the higher strike price paying for the call bought at the lower strike price.
If the stock at expiry is above the strike price of the sold calls the stock is sold at this level. The remaining option position is a bull call spread that achieves its maximum profit at this same price. Profits from the bull call spread and the partial recovery in the stock allow the investor to break-even at a lower price than if the investor had simply continued to hold the stock.
Other considerations
- Time decay: time decay works against the buyer of the call. If the expected share price rise does not take place soon after entering the position, time decay will start to erode the value of the option.
- Strike price: the investor will usually have a choice of strike prices, and must balance the cost of the option against the rise in share price required for the strategy to be successful. The out-of-the money option will be the cheapest, but also requires the largest rise in share price. Many investors regard the at-the-money option as offering the best balance of risk and reward.
- Expiry month: a longer-term option allows more time for a rise in the share price to take place, but will be more expensive than a shorter-term option. The investor needs to form a view of the time frame over which the share price movement is expected to take place.
Follow-up action
If the share price at expiry is below the strike price of the sold options, these options will expire worthless, and the investor has only to close out the bought call to recover any intrinsic value.
If the stock price is above the strike price of the sold calls, the investor will need to close out one or both of the written legs. The investor may allow one of the calls to be exercised if they wish to exit their stock position. The bought call will also need to be closed out to recover intrinsic value.
Points to remember
- This strategy is suitable if your investment goal is to break-even and sell the stock.
- The strategy benefits from a small upward movement in the market. It should not be used if a strong upward movement is expected.
- If the stock continues to fall, the strategy does nothing to alleviate further losses on the stock.