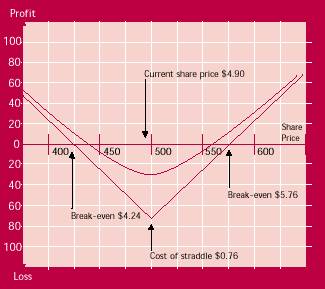
Profits and losses
At expiry, the investor will make profits if the share price has moved strongly enough in either direction. Profits can be taken early in the life of the straddle, but only if the expected movement occurs quickly. As the market moves strongly in one direction, the gain made on one leg exceeds the loss incurred on the other, and the straddle increases in value.
Other considerations
- Time decay: the bought straddle consists of two long positions. As a result, time decay works strongly against the strategy. The longer the straddle is left in place, the greater the loss due to time decay. The position must therefore be closely monitored and may need to be closed out well before expiry.
- Expiry month: the investor must balance the cost of the strategy against the time needed to give it the best chance of success. The more distant expiry months will provide the strategy with more time, however longer dated options will be more expensive than those with shorter dates.
Follow-up action
The taker of a straddle expects volatility in the market to increase. Only rarely will this strategy be held to expiry. If the investor's market view proves correct, the straddle should be unwound to crystallise the profits. The position can be liquidated on both sides simultaneously or, if the out-of-the-money option has little value, it could be left open in case the market were to reverse.
If volatility does not increase as expected, the strategy should be taken off well ahead of expiry, before time decay damages the position.
Points to remember
- Choose options over shares you expect to remain or become volatile.
- Select an expiry month that gives the strategy time to work.
- Monitor the position closely and be prepared to unwind it well before expiry.