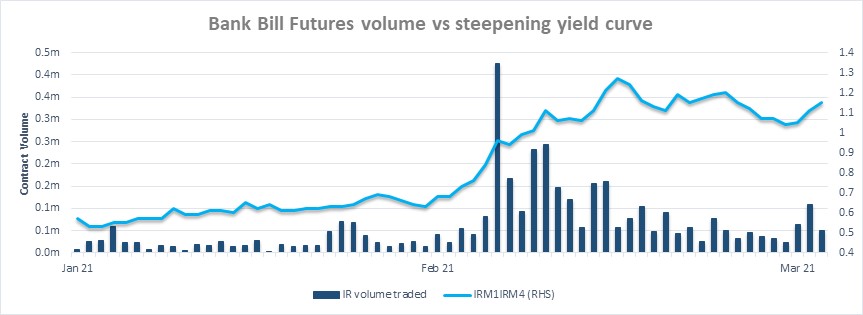
The increase in inflation expectations was largely driven by positive sentiment around the roll out of vaccines and key economic data, driving a selloff in global bond markets. The longevity of the RBA’s Yield Curve Control (YCC) program was challenged with yields increasing on the target YCC lines. The RBA purchased YCC bond lines for the first time since December in order to contain bond yields at the front of the curve. This impacted liquidity and pricing in both the physical and futures market, resulting in challenging conditions going into the quarterly roll.
The RBA reiterated its monetary policy stance multiple times, confirming they do not expect to raise the Cash Rate for at least another 3 years. The RBA also made changes to the cost and mechanism by which YCC lines can be borrowed by market participants. Bond yields on the YCC lines have since fallen to around 10 basis points in alignment with the YCC target yield. Overall risk appetite appears to have declined in March, impacting Open Interest and activity across the futures complex.
Interest in the 5 year Bond Future remains strong with an increasing range of participants trading the product. Going into the roll period, Open Interest reached 108,000 contracts while ADV reached 12,000. Activity in the second half of March was more subdued, likely driven by reduced demand for mid curve bonds given speculation around rising yields and lower levels of risk appetite more broadly.
March Bond Roll
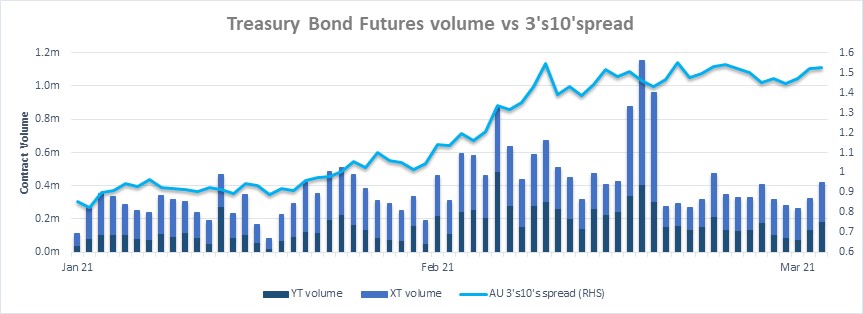
The March roll represented the third roll with reduced tick increments for the 3 and 10 year Bond Futures. Overall roll volumes were lower, particularly in the 3 year contract, driven by challenging conditions in the physical bond market and reduced risk appetite. Despite these difficulties, the bond roll was orderly and well spread throughout the 5 day period with the finer tick increments delivering significant cost savings to end users.
- Top of book liquidity and order book depth were lower across all contracts due to increased volatility.
- 3 and 10 year roll volumes were down 25% and 8.3% respectively when compared to December 2020. Bond roll liquidity in the 3 and 10 year contracts was commensurate with levels seen at the height of the pandemic in March 2020, reflecting the extremity of market conditions.
- Open Interest in both contracts declined following the roll reflecting reduced risk appetite.
- 114,575 3 year contracts and 45,840 10 year contracts were taken to cash settlement.
A total of 93,957 90 Day Bank Bill Futures contracts were taken to cash settlement, an increase of 9% vs December 2020.
OTC swap volumes
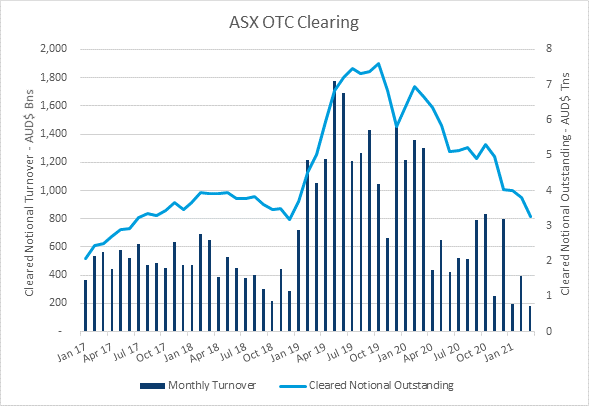
Global AUD OTC swap volumes continue to be lower driven by a significant decrease in shorter-date interest rate swap and OIS volumes as a result of the low rate environment and yield curve control. ASX’s OTC Clearing service has recorded total notional cleared of A$770bn in Q1 2021.
ASX has grown its activity and market share in longer dated interest rate swaps, with Weighted Average Maturity of ASX Cleared Interest Rate Swaps growing 81% to 2.35 years across the 12 month period ending March 2021 with market participants taking advantage of ASX’s lower total cost of clearing and the available cross-margining offsets (average 45% cross-margining benefit across users of ASX’s Margin Optimisation service).
Effective, 12 April 2021, ASX added support for 5-year bond futures cross-margining - further improving the efficiency available from ASX’s Margin Optimisation Service. In a simple example of a DV01 equivalent position in 5 year bond futures offsetting a 5 year ASX-Cleared OTC Interest Rate swap (5 year swap EFP), a minimum initial margin reduction of 63% will be achieved when compared to clearing the positions separately.